Day 2 of the 90-day challenge
we explore Linux, an operating system that serves as a mediator by offering an interface and services that allow users to engage with computer hardware and software. By abstracting technical complexities, enforcing access control, and providing a flexible environment, Linux enables effective computer usage. As a free and open-source operating system, it is suitable for personal computers and workstations, boasting professional-level internet services, comprehensive development tools, a fully functional graphic user interface, and a wide array of applications, including office suites and multimedia applications.
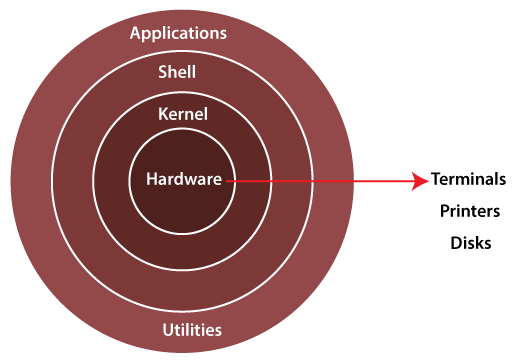
The Architecture of Linux
1 Hardware Layer:
The hardware layer, the lowest layer in the Linux architecture, encompasses all physical components of the computer, including the CPU, memory, storage devices, network adapters, and peripherals. It directly interacts with the Linux kernel, supplying the necessary resources and infrastructure for the operating system and user-level applications to operate effectively.
2 Kernel Layer:
The kernel, as the core of the Linux operating system, acts as an intermediary between the hardware and user-level software, providing essential functionality for effective operation. Its key responsibilities encompass process management, memory management, file system operations, hardware device management, and system security. By controlling access to hardware resources, scheduling processes for execution, and managing system services, the kernel ensures seamless interaction between the Linux architecture and user-level applications.
3 Shell Layers:
The shell serves as the user interface to the Linux operating system, offering a command-line interface (CLI) that enables users to interact with the system. Through the shell, users can input commands that are subsequently interpreted and executed, while also benefiting from its management of processes and handling of input and output operations.Common Linux shells include Bash, Zsh, and Fish.
4 Application Layer:
The majority of the Linux structure consists of user-level apps and tools, including various software such as text editors, web browsers, office programs, development tools, and system management utilities. Users and apps interact with the Linux system using these software components, aided by command-line interfaces (CLI) such as Bash, Zsh, and Fish. These CLIs allow users to input commands that are subsequently interpreted and executed while managing processes and handling input and output operations.
Linux Distributions
There are several different Linux distributions.
Different companies and groups have packaged Linux and Linux software in significantly different ways.
Here are some of the most popular and widely recognized Linux distributions:
1 Ubuntu:-
Ubuntu is famous for being easy to use and very popular. It uses the GNOME desktop but has other options too. A big community and a company called Canonical Ltd. help users and apps work with Linux using software parts and command tools like Bash, Zsh, and Fish.
2 Debian:-
Emphasizing stability and open-source principles, Debian offers different branches such as "Stable," "Testing," and "Unstable" to cater to various levels of software stability. It also provides the APT package management system for efficient software management.
3 Fedora:-
Features the latest open-source software and technologies. Maintained by the Fedora Project, a community-driven initiative with Red Hat's support Uses the GNOME desktop environment as the default.
4 CentOS:-
A free and open-source enterprise-class Linux distribution It is often used in server environments due to its stability. It provides long-term support and is closely related to Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
5 Kali Linux:
Designed for penetration testing and digital forensics Includes a wide range of security and hacking tools. Maintained by Offensive Security
What is an operating system?
An operating system is a program that manages computer hardware and software for users.
What is Open source?
Open source means that the source code for an application is freely distributed along with the application.
Basic Linux Commands
ls : List files and directories in the current directory.
ls -la : List all files or directories including hidden files.

cd: Change the current working directory.

pwd: Display the current working directory.
mkdir: Create a new directory.

rm : Remove an empty directory.
cp : Copy files and directories.
mv : Move or rename files and directories.
cat : Display file content.

mkdir -p : Create nested directory A/B/C/D/E

Happy learning